Home > News > Industry News > From science fiction to reality, how flexible sensors shape the future of human-computer interaction and smart devices
From science fiction to reality, how flexible sensors shape the future of human-computer interaction and smart devices
With the rapid advancement of science and technology, humanoid robots are gradually moving from science fiction into reality. As key players in human-machine interaction and automation, the development of humanoid robots reflects a country's scientific and technological prowess. Tactile perception, a crucial means for humans to interact with the outside world, is crucial for achieving a high level of intelligence and anthropomorphism in humanoid robots. The emergence of flexible sensors has revolutionized tactile perception in humanoid robots, enabling them to interact with their environment and humans more precisely and naturally.
Overview
1. Working Principle of Flexible Sensor
Flexible sensors are a type of sensor that can maintain stable performance despite deformations such as bending, folding, and stretching. Their operating principle is that when a material is exposed to external stimuli (such as pressure, temperature, and humidity), its physical or chemical properties change, converting these properties into detectable electrical or optical signals. For example, resistive flexible sensors detect pressure by measuring how the material's resistance changes with pressure; piezoelectric flexible sensors utilize the material's piezoelectric effect to generate an electrical charge when subjected to pressure.
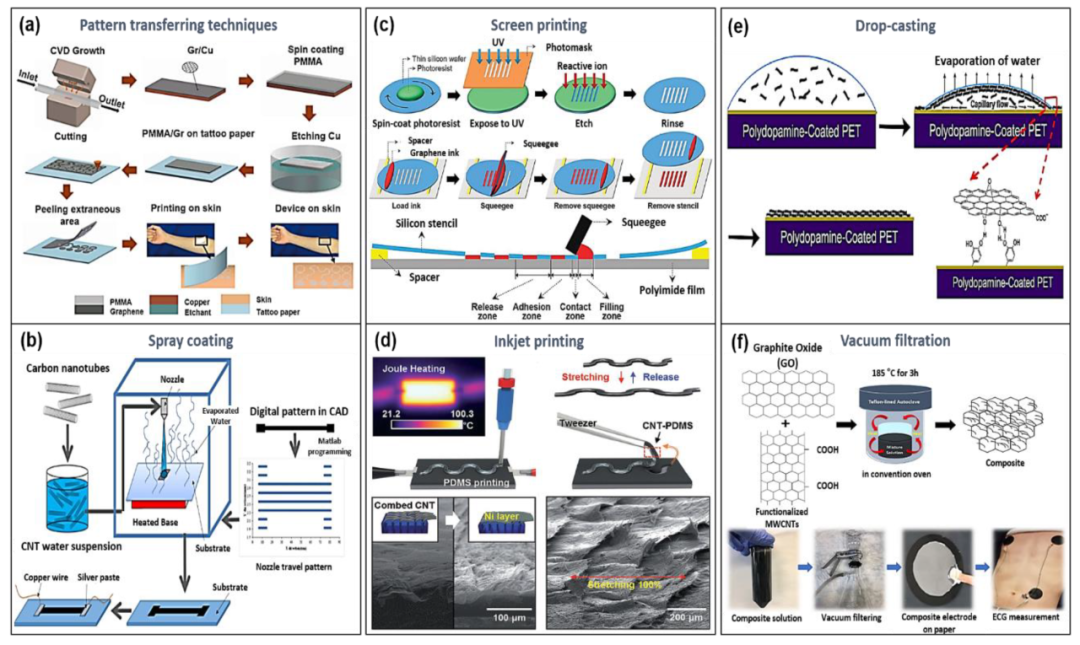
Manufacturing process of flexible sensor:
2. Advantages of flexible sensors over traditional sensors
Compared to traditional rigid sensors, the greatest advantage of flexible sensors lies in their exceptional flexibility. They can easily conform to a variety of irregular surfaces and maintain stable operation even when objects undergo dynamic deformation. For example, in wearable devices, flexible sensors can comfortably fit human skin and monitor physiological signals such as heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature in real time without causing any discomfort to the user or affecting the normal operation of the device. In the industrial field, they can be installed in the joints of robotic arms, bending and deforming with the arm's movement, accurately sensing the joint's motion and force conditions, providing critical data support for precise control.
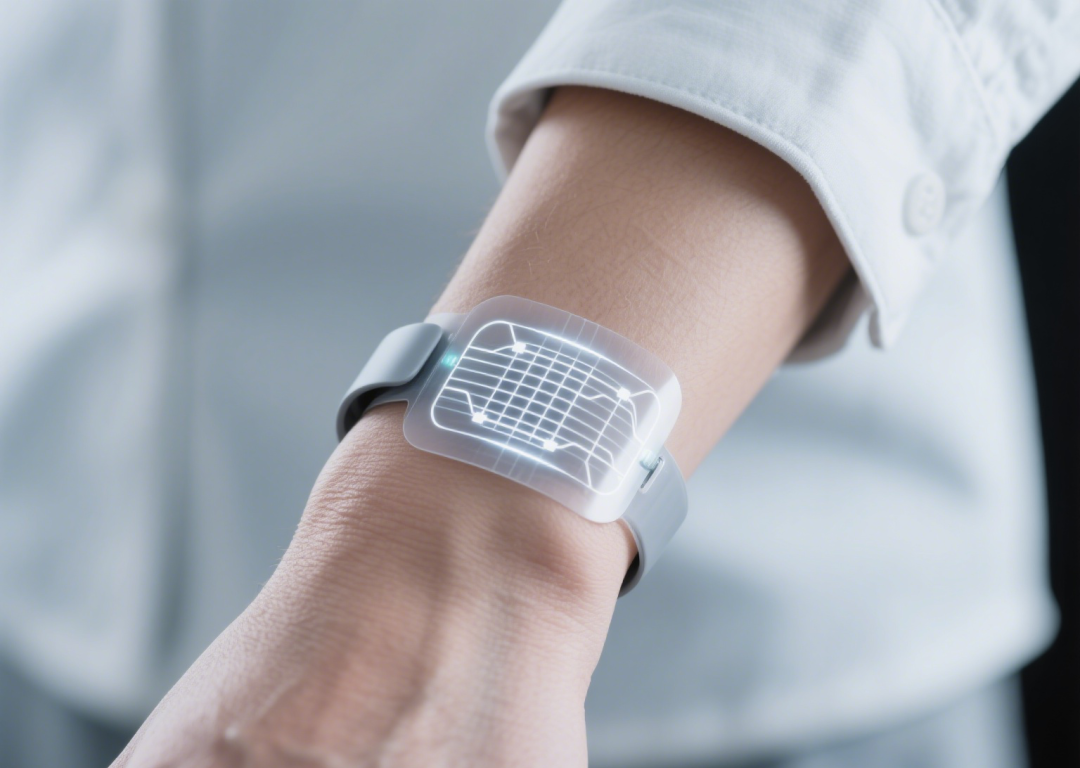

3. Flexible sensors are the key to giving robots or dexterous hands the ability to perceive
Electronic skin needs to mimic the tactile and perceptual abilities of human skin. Flexible sensors can detect pressure, temperature, humidity, and chemical substances, converting these physical or chemical signals into electrical signals, providing the foundation for robots to interact with the outside world. For example, through the piezoresistive and capacitive effects, flexible sensors can sense pressure and deformation. They can also detect temperature and humidity to translate these changes in the environment. They can also sense the properties of objects and convert them into electrical signals. Furthermore, the performance of flexible sensors directly impacts the overall performance of the electronic skin.
Five technical routes for flexible sensors
There are currently five mainstream flexible sensor technology routes on the market, namely resistive, capacitive, piezoelectric, optical and Hall effect sensors.
1. Resistive Flexible Sensor
Resistive flexible sensors work by detecting changes in the resistance of conductive materials when they are subjected to force or deformation. When the sensor is bent, stretched, or compressed, the length and cross-sectional area of the conductive path within it change, resulting in a change in resistance. By measuring this change in resistance, the force or deformation applied to the sensor can be inferred. This type of sensor, with its simple structure and fast response, is commonly used in wearable devices, electronic skin, and robotic tactile systems.
2. Capacitive Flexible Sensor
Capacitive flexible sensors operate based on the principle of capacitance change. They typically consist of two layers of conductive electrodes separated by a flexible insulating medium. When the sensor is bent, stretched, or compressed, the distance between the electrodes or the overlapping area changes, altering the capacitance. By detecting this capacitance change, strain or pressure can be accurately measured. Capacitive flexible sensors offer the advantages of high sensitivity and low power consumption, making them suitable for applications such as precision pressure detection and gesture recognition.
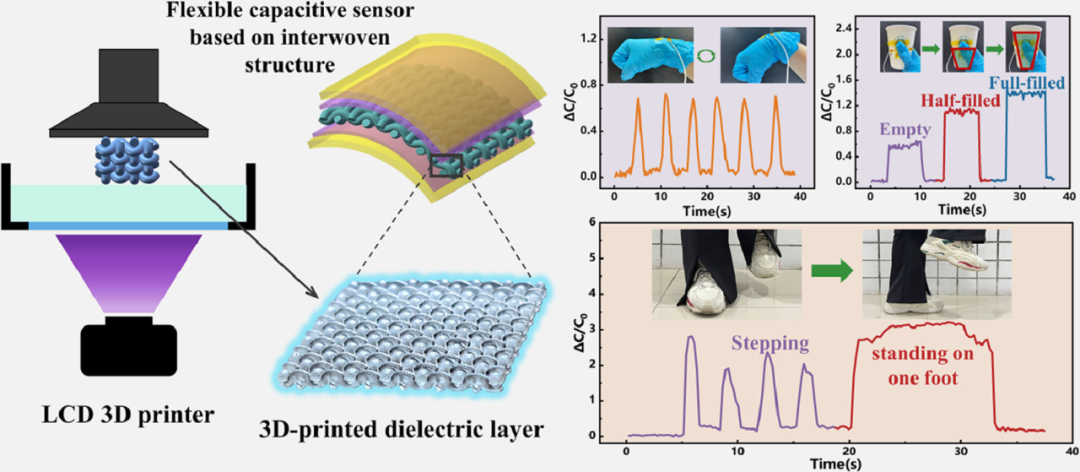
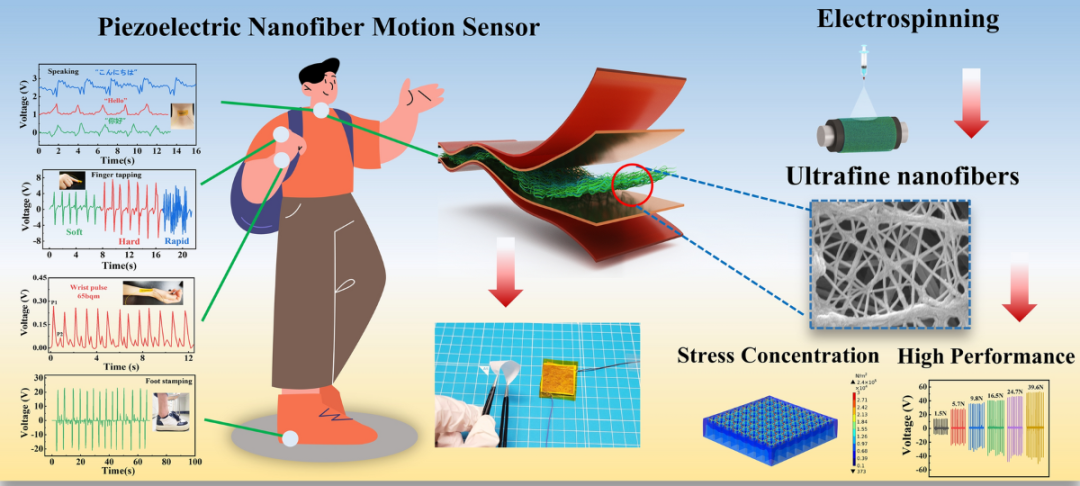
3. Piezoelectric Flexible Sensor
Piezoelectric flexible sensors utilize the piezoelectric effect, the property of generating an electric charge signal when subjected to force or mechanical strain. When the sensor is compressed, stretched, or bent, the electric dipole moment within the piezoelectric material changes, generating a voltage output across the electrodes. By measuring this voltage, force, vibration, or shock can be monitored. Piezoelectric flexible sensors offer fast response and a wide frequency range, making them commonly used for vibration monitoring, tactile sensing, and dynamic pressure detection.
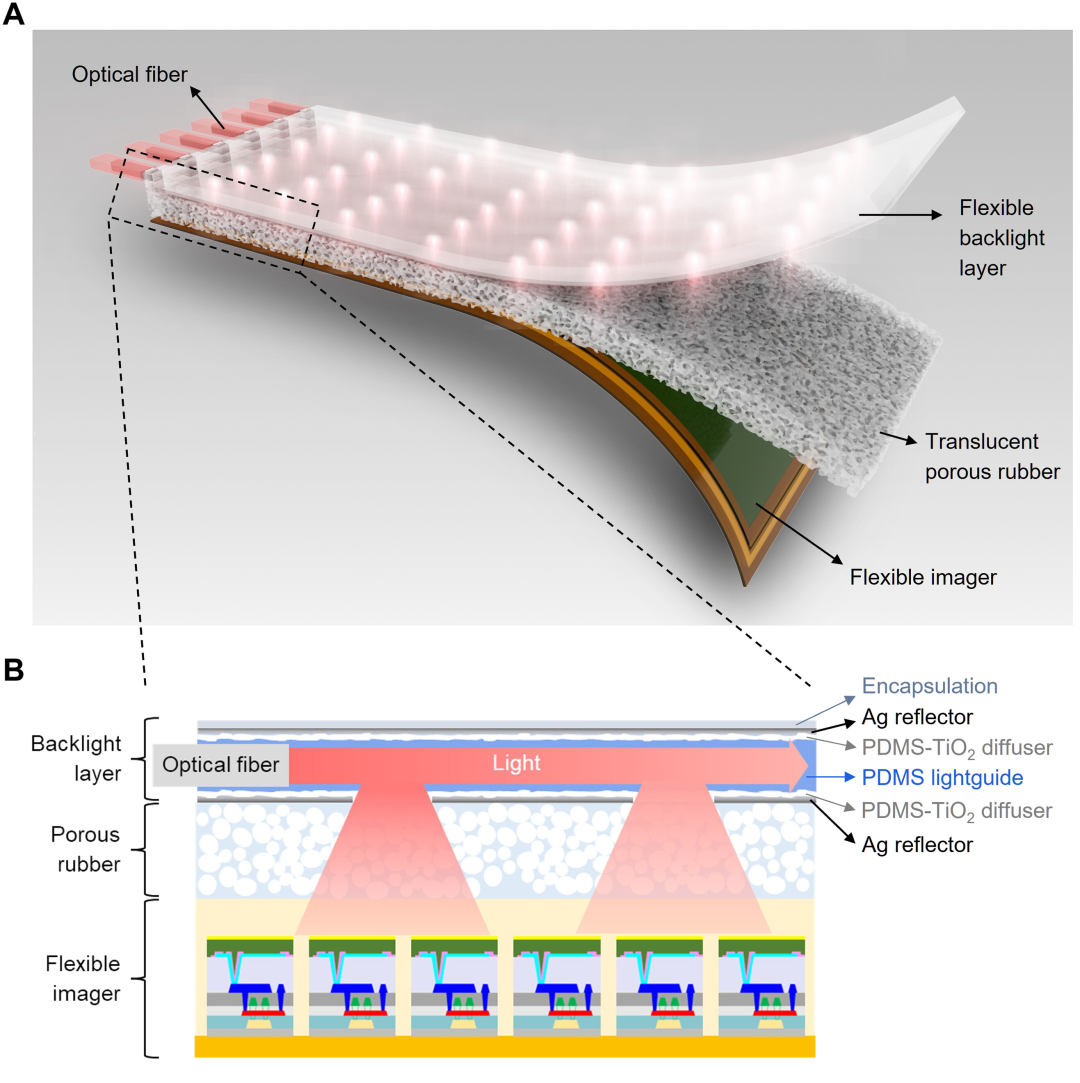
4. Optical Flexible Sensor
Optical flexible sensors measure by changes in optical signals. They typically consist of a light source, a flexible light guide or optical fiber, and a light detector. When the sensor is bent, stretched, or compressed, the light propagation path, intensity, or interference conditions within the light guide change, causing the detected optical signal to change. By analyzing these changes in the optical signal, the applied force, displacement, or strain can be inferred. These sensors offer advantages such as immunity to electromagnetic interference and high sensitivity, making them suitable for medical monitoring and wearable devices.
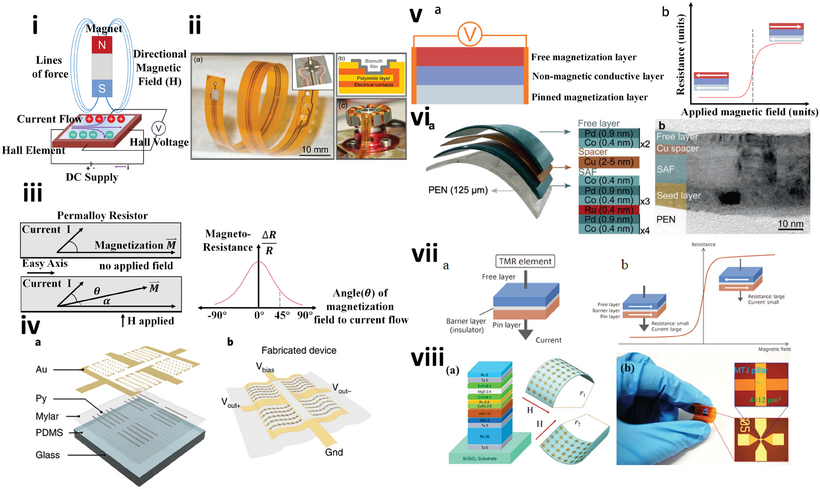
5. Hall Effect Flexible Sensor
Flexible Hall-effect sensors operate based on the Hall effect principle, which states that a conductor or semiconductor, exposed to a magnetic field, generates a voltage perpendicular to the current. Flexible Hall-effect sensors typically incorporate magnetic materials or micromagnets onto a flexible substrate. When the sensor is bent or moved, the magnetic field distribution changes, causing the output voltage to change. By detecting this voltage change, displacement, angle, or force can be measured. Flexible Hall-effect sensors are widely used in smart wearables, robotic positioning, and gesture recognition.
Market size
1. International giants dominate, while the rise of domestic forces accelerates the restructuring of the industrial landscape
The flexible tactile sensor industry has relatively high technical barriers, long R&D cycles, and a relatively concentrated market structure, with high-end production capacity dominated by foreign companies. According to QYReaearch data, the top five manufacturers in the global flexible tactile sensor market in 2022 will include Novasentis, Tekscan, Japan Display Inc. (JDI), Baumer, and Fraba, collectively holding approximately 57.1% of the market share. With the booming humanoid robotics industry, flexible sensors, as a core component, have broad market prospects, and domestic companies are actively developing this field. Companies such as Hanwei Technology, Shenhao Technology, Keli Sensing, Fulai New Materials, Pasini, Newdirui, Titanium Deep Technology, and Puhui Technology are already actively involved in the flexible sensor field, seizing market opportunities through various means, including technological research and development, industrial collaboration, and ecosystem development.
While international giants currently dominate the flexible tactile sensor market, the accelerated expansion of domestic companies is injecting new vitality into the industry. With the continued deepening of technological research and development and the strengthening of industry chain collaboration, domestic companies are expected to achieve breakthroughs in core technologies, gradually breaking the international monopoly and promoting a diversified competitive and innovative global market for flexible tactile sensors. This will provide more cost-effective and adaptable core components to support the development of downstream industries such as humanoid robots.
2. Flexible sensors are widely used in many fields, and the market size is growing year by year
In the consumer electronics sector, flexible sensors provide core support for touchscreen controls in foldable phones and health monitoring in smartwatches. In healthcare, the high compatibility of flexible materials with human skin makes them ideal for wearable devices, from heart rate monitors to smart bandages. In the automotive industry, flexible sensors enable the upgrading of in-vehicle interactive systems, with applications such as steering wheel touch and seat pressure sensing enhancing the driving experience. In industrial automation, flexible sensors can conform to the surfaces of irregularly shaped equipment for precise detection, playing a vital role in robotic grasping and assembly line quality monitoring. The collaborative penetration of these multiple sectors is transforming flexible sensors into one of the most promising growth sectors in the intelligent era.
Data Bridge Market Research data shows that the global flexible sensor market size has been increasing year by year, reaching a basic scale in 2022 and is expected to reach US$9.04 billion by 2029. Demand from fields such as medical care and robotics has become a key driving force for market growth.
3. From Policy to Application: Current Status and Prospects of China’s Flexible Sensor Industry
With the upgrading of domestic manufacturing and the increasing demand for intelligent technology, the application of flexible sensors in various fields will continue to expand. The Chinese government has always attached great importance to the development of new materials, new energy, and new technologies, and has also introduced a series of supporting policies. These policies will further promote the development and growth of China's flexible sensor industry. According to Zhiyan Consulting, the market size of China's flexible sensor industry is growing rapidly, reaching 2.112 billion yuan in 2022. The market is mainly distributed in North China, Central and South China, and East China, accounting for 19.84%, 34.66%, and 27.79% respectively.
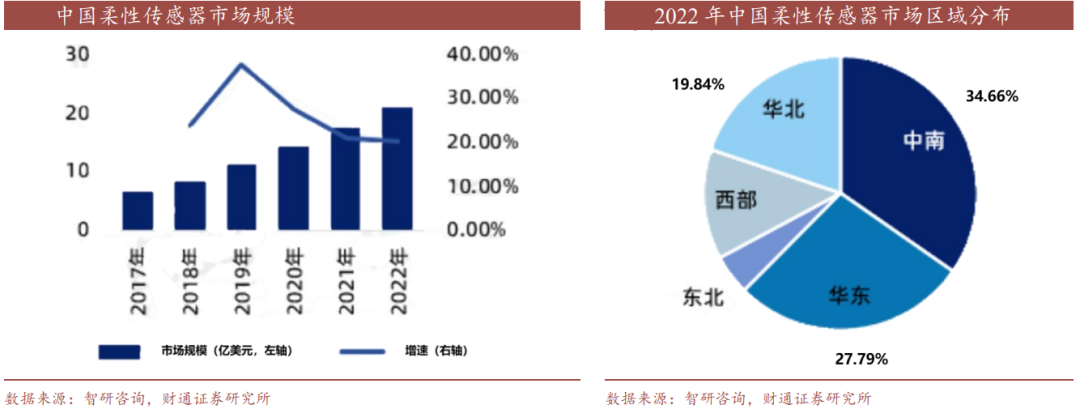
图源:智研咨询
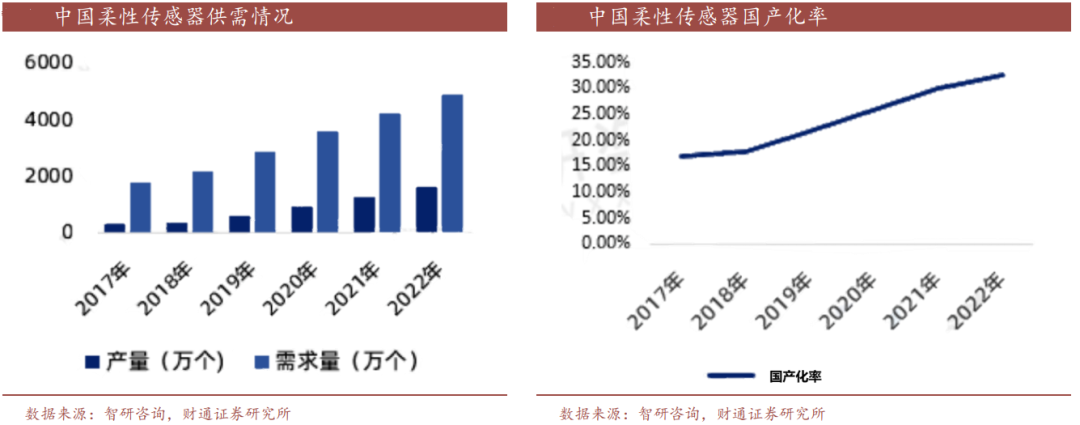
China is one of the world's largest markets for consumer electronics. Flexible sensors are increasingly used in consumer electronics products such as smartphones, wearable devices, and smart homes, and are expected to see further development in emerging sectors. For example, the rapid development of industrial automation and robotics in China will drive the growth of flexible sensors in industrial applications. According to Zhiyan Consulting, demand for flexible sensors in China will reach 49.231 million units in 2022, with an annual production of 16.34 million units. The localization rate of flexible sensors in China is also gradually increasing, reaching 32.50% in 2022.
图源:智研咨询
Conclusion
With continuous technological breakthroughs and the growing demand for intelligent devices across various fields, flexible sensors, as a key bridge connecting the physical world and digital intelligence, are experiencing unprecedented development opportunities. From enabling humanoid robots to achieve human-like tactile perception to playing an irreplaceable role in consumer electronics, healthcare, industrial automation, and other scenarios, the application boundaries of flexible sensors are constantly expanding, and the market size is steadily growing, driven by both policy support and technological advancements.
Although there is still a gap between domestic and international advanced levels in terms of high-end material consistency and long-term reliability, these bottlenecks are expected to be gradually overcome with the gradual increase in the localization rate and continued growth in R&D investment. In the future, with the deepening of multimodal sensing technology, the optimization of manufacturing processes, and the rational control of costs, flexible sensors will be more widely integrated into all aspects of production and life. This will not only propel cutting-edge fields such as humanoid robots towards a new stage of greater intelligence and anthropomorphism, but will also inject core power into humanity's construction of a more efficient, convenient, and warmer intelligent interactive world. The development of flexible sensors is writing a new chapter in the era of human-computer interaction, and their potential and value will continue to flourish in the tide of scientific and technological progress.
You can change these settings at any time.